Environment Variables On Elastic Beanstalk with nodejs
26 Mar 2016It's recommended to avoid storing configuration settings such as private keys and secrets in the code base. A good solution is to use environment variables to store these settings and then access them from your code.
Elastic Beanstalk lets you enter the environment variables for each environment using the management panel.
On AWS, open Elastic Beanstalk. Go to your
Application > Environment > Configuration > Software Configuration. Under
Environment Properties you will find a list of properties you can configure.
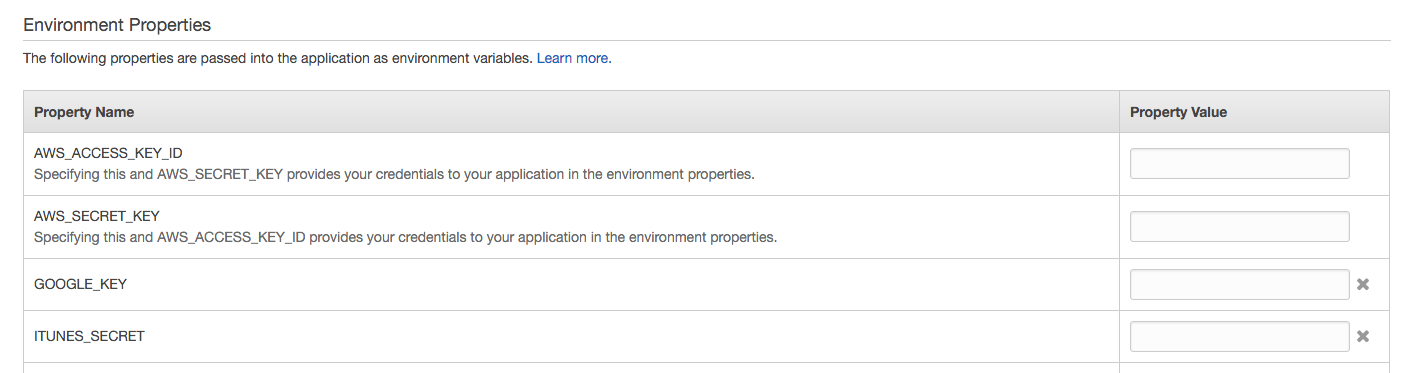
These variables will be attached to the process.env object. Then, you can read these variables
like you would read any environment variables from your configuration file:
const config = {};
config.db = {
database : process.env.DB_DATABASE || 'my_db',
host : process.env.DB_HOST || '33.33.33.1',
port : process.env.DB_PORT || 3306,
user : process.env.DB_USER || 'root',
password : process.env.DB_PASSWORD || 'root',
};
export default config;
In the example above, the config object will have the elastic beanstalk variables if they exist (when the code runs on elastic beanstalk) and will have the provided local variables as a fallback (when the code runs locally for example).
This way you can avoid committing the production settings to your code base.
As an alternative to using this UI, you can also set the environment variables using .ebextensions.